Assets under management at BlackRock reached a record $11.5 trillion at the end of the third quarter of this year, boosted by net inflows to fixed income strategies and exchange-traded funds.
Laurence Fink, chairman and chief executive of BlackRock, said on the third quarter results call on 11 October that assets under management have risen $2.4 trillion year-over-year, driven by $456bn of net inflows and positive market movements. Total net inflows in the first nine months of this year were $360bn, which was more than full-year net inflows in both 2022 and 2023.
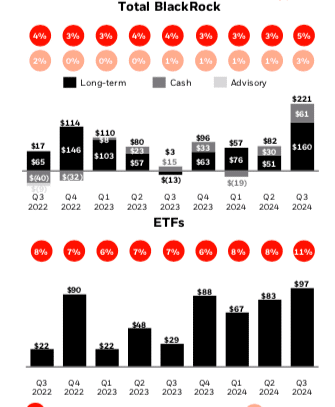
BlackRock had $456bn of net inflows in the last 12 months, including a record $221bn in the third quarter, which represented 8% annualized organic asset growth. Net inflows were positive across client type, product type, active and index, and regions according to Fink.
He said: “Organic growth is accelerating as we execute on a strong pipeline and clients turn to Blackrock to move in size. The opportunities ahead have never been better than we see now.”
Fink described public and private markets; iShares, the ETF franchise; whole portfolio outsourcing and its proprietary technology platform, Aladdin, as structural growers which are poised to accelerate to year end, as the fourth quarter is typically the strongest for BlackRock.
Martin Small, chief financial officer, said on the results call that iShares leads the industry in global flows, with approximately $250bn in net inflows in the first nine months of this year, which is 40% more than historical total annual flows. ETF net inflows were $97bn in the third quarter, with $48bn into fixed income. Fink added that on a stand-alone basis, BlackRock’s fixed income ETF platform would be in the top five.
Small said: “iShares’ fixed income assets now stand at over $1 trillion, nearly 40% higher than at year-end 2021.”
Fixed income delivered over $60bn of net inflows across BlackRock and the firm believes a continued path of central bank normalization will support sustained inflows across bond funds and ETFs.
“Fixed income remains a compelling organic growth opportunity for BlackRock,” said Small.
In the third quarter, BlackRock launched a spot ethereum ETF, which Fink said has gathered more than $1bn in assets in the first two months of trading. BlackRock’s Bitcoin ETF, which launched in February this year, has grown to $23bn.
Private markets
BlackRock closed the acquisition of Global Infrastructure Partners on 1 October 2024, adding $116bn of client assets under management and $70bn of fee-paying assets under management. Fink said the firm is already seeing the power of BlackRock and GIP together as it drives increased access to the enormous investment potential of infrastructure, especially to support AI innovation. GIP is expected to add approximately $250m of management fees in the fourth quarter according to Small.
“We believe we are building the model portfolio solution that will democratize retail access to private markets,” Fink added. “And our planned acquisition of Preqin will enhance data and risk analytics needed to support growing private markets allocations.”
Small described private markets as a strategic priority for BlackRock. He added that the closure of the GIP acquisition triples BlackRock’s infrastructure assets under management and doubles private markets’ run-rate management fees.
In June this year BlackRock announced a £2.55bn acquisition of Preqin, an independent provider of private markets data. At the time Fink said that BlackRock wanted to bring the principles of indexing, and even iShares, to the private markets. He added: “We anticipate indexes and data will be important future drivers of the democratisation of alternatives, and this acquisition is the unlock.”
In September this year BlackRock, GIP, Microsoft, and MGX, an Abu Dhabi-based artificial intelligence and advanced technology investor, announced the Global AI Infrastructure Investment Partnership. It will make investments in new and expanded data centers to meet growing demand for computing power, as well as energy infrastructure to create new sources of power for these facilities. The partnership will initially seek to unlock $30bn of private equity capital with the intention of mobilizing up to $100bn in total investment potential when including debt financing. Small cited the partnership as the first example of the growth synergies that BlackRock and GIP can create.
There is also growth potential in providing access to private markets to wealth plans. BlackRock manages more than $300bn of assets across model portfolios and separately managed accounts for wealth managers, which could benefit from increased exposure and more efficient access to the asset class.
“We believe the model portfolio solution will revolutionize access to private markets for wealth managers and improve portfolio outcomes for millions of households,” said Small.
The announced acquisition of Preqin will accelerate this potential by providing private markets’ data and analytics. Small said the deal is due to close at the end of this year, subject to regulatory approvals.
Fink continued that BlackRock has never shied away from making big bets to better serve clients, such as creating technology platform Aladdin and unlocking new markets through ETFs. He said client enthusiasm for the planned integration of GIP has exceeded BlackRock’s own high expectations and predicted that their private market allocations will continue to grow as they want inflation-protected long-term returns. In addition, Fink said standardized, transparent data and analytics will become increasingly important.
“The growth of private markets is underpinned by the continued rise of infrastructure which presents a generational investment opportunity,” added Fink. “$75 trillion is needed to repair ageing infrastructure, and to invest in data centers and decarbonization technology.”
In addition, BlackRock has an $85bn private credit platform, which Small said is a huge growth opportunity, particularly with insurance clients.
“We are the largest core fixed income manager in the world for insurance companies and manage $700bn of insurance company general account assets,” Small added. “If we can flip just 10% into private credit strategies, that is $70bn of opportunity sitting with existing clients in the capabilities we have today.”
Financials
Third quarter revenue and operating income were both records. Revenue increased 15% year-over-year to $5.2bn, which BlackRock said was driven by the positive impact of markets on average assets under management, organic base fee growth, and higher performance fees. Operating income increased 23% year-over-year to $2bn. BlackRock expanded its margin by 45.8% to 350 basis points year-on-year and the firm generated 5% annualized organic base fee growth, the highest for a quarter in three years.
Small said that in the third quarter one large US asset manager selected BlackRock’s proprietary technology platform, Aladdin, to unify its investment management technology across public and private markets.
“Our results highlight the power of Aladdin as a unifying technology,” said Small. “Aladdin enables new capabilities to drive top-line business growth for clients, while also unlocking scale and efficiency.”
In October Royal Mail Pension Plan said it has launched the UK’s first Collective Defined Contribution (CDC) scheme and appointed BlackRock as investment manager of the plan. Sarah Melvin, head of UK & Europe at BlackRock, said in an email: “The certainty of an income for life that Collective Defined Contribution schemes provide will be deeply reassuring for many, and we applaud Royal Mail, the Trustees, the Communications Workers Union and Unite CMA for the innovation and work they have undertaken to introduce this to the UK.”
Cash management had net inflows of $61bn in the third quarter. Fink said many investors have large cash holdings but will have to re-risk to meet their long-term return needs by investing in opportunities in technology, AI and the unprecedented need for new infrastructure.
“Blackrock is exceptionally well positioned in front of that $9 trillion of money market funds across the industry,” Fink added. “As that cash makes its way into public and private markets, we are connecting our clients to opportunities and working with them in an integrated portfolio to help them deploy their capital.”
Small argued that BlackRock has historically delivered outsized organic growth in periods of investor rerisking, around election cycles and changes in central bank policy and the fourth quarter has also been historically strong for inflows.


















Beyond Fundamental Analysis: What Does it Take for Active Traders to Get an Edge in Stock Markets?
By David Russell, Global Head of Market Strategy, TradeStation
Volatility may be an everyday occurrence in global markets, while it can make life difficult for traders to decisively determine where stock prices are headed. But active traders who look beyond fundamental analysis by working within a framework, can often quickly understand any business, in any sector. Going outside traditional comfort zones can help traders unravel the mystery as to what’s moving prices that may be a route to profitable trades. Here’s why.
For active traders, price action reigns supreme. Whether trading on momentum or dissecting chart patterns, the “why” behind stock movement often takes a backseat to the fact it is moving at all. But here’s the kicker: understanding the major forces behind those moves – like economics and market fundamentals – can be a game-changer. Breaking down the drivers underlying price swings can offer a new perspective and an extra edge, morphing chaos into structured opportunity. It’s another potential tool in the arsenal that can help lead to more informed trades.
Using a playbook to identify stocks that are signaling a breakout provides an unemotional mindset for active traders to help decide whether a trade is good or bad. This eliminates some of the need to pore over analysts’ reports and time-consuming research that, in many situations, can be overwhelming and might limit how quickly a trader can react.
Instead, active traders working against a roadmap are often better positioned to act on sudden changes in sentiment toward individual stocks or the overall market. One could liken this mindset to how triaging takes place in the ER to quickly decide which patients need the most immediate help. Traders who adopt a framework can quickly wrap their heads around understanding what is needed to make trading decisions.
So what does this framework look like?
Here are seven catalysts that can help give traders a head start. Let’s call this framework ‘The Catalyzers.’
Let’s take a look at some recent examples of the system in action.
Volumes
GenAI has led to a surge in investor appetite for tech stocks. NVIDIA has become a sales growth machine and a bellwether for the AI sector. Since early 2023, the chipmaker’s GPU quarterly revenues have stunned markets, achieving a blistering 265% year-on-year growth in the fourth quarter of last year. That capped increases of 206% and 101% in the two preceding quarters, and the growth story has continued this year. With its stock price up around 3000% since 2019, NVIDIA is a prime example of how changes in volumes can propel stock prices.
Margins
Meta has cut around 13% of its workforce during the last year. The tech giant is engaged in an ongoing round of belt-tightening that with the reduction in headcount, has substantially boosted profits. For example, Meta’s net income more than tripled to $14 billion, or $5.33 per share, from $4.65 billion, or $1.76 per share, a year earlier when it reported its Q4 2023 earnings in February of this year. Taken together Meta’s actions saw profits rise faster than revenues as a result of the cost cutting measures. The surge in profits also led Meta to declare a dividend and signal that it would be buying back more stock, a strategic development which is discussed below.
Macroeconomic events
The Federal Reserve cut interest rates for the first time in four years in September and is signaling another 50 basis points could take place this year. Rising interest rates led to a bear market in 2022, but lower inflation has since improved the macro rate outlook, allowing the stock market to recover. This clearly demonstrates how the macro environment can impact stock prices. Additionally, interest rates are a proxy for sentiment surrounding small caps and gold prices. With expectations that the Fed will continue to reduce rates into 2025, and the looming U.S. presidential election in November, these are potentially market-moving developments that could transcend individual companies. A spike in oil prices could also be a major event that may impact stock markets.
Strategic developments
Kellanova (K), a leading company in global snacking, international cereals and noodles, North American plant-based foods and frozen breakfast foods, recently agreed to be acquired by Mars, Incorporated, for a total consideration of $35.9 billion. Kellanova shareholders will receive $83.50 per share in cash, which represents a 33% premium to the stock’s closing price as of August 2, 2024. This acquisition was made possible by Kellanova’s prior spinoff, which unlocked value and breathed new life into what was considered ‘dead money.’ For active traders, the transaction could present some interesting trading opportunities.
Business transformation
Walmart reported strong sales and beat estimates in its latest quarterly earnings report. Of note was a 21% year-on-year increase in e-commerce revenues and is an example of a business undergoing transformation. Walmart is embracing tech in a big way, including the use of generative AI. Using Large Language Models (LLMs), Walmart was able to create or improve 850 million data sets – a task that would have required 100 times the current headcount to analyze everything from shelf trends to customer buying habits. With Amazon in its sights, Walmart is overhauling its business model.
With so much noise in financial markets, understanding what’s moving prices can help traders evaluate stocks in sectors that they may not usually consider. Using the ‘triage’ methodology alleviates some of the need for detailed analysis, potentially helping active traders to quickly determine a plan that might be a pathway to higher returns.